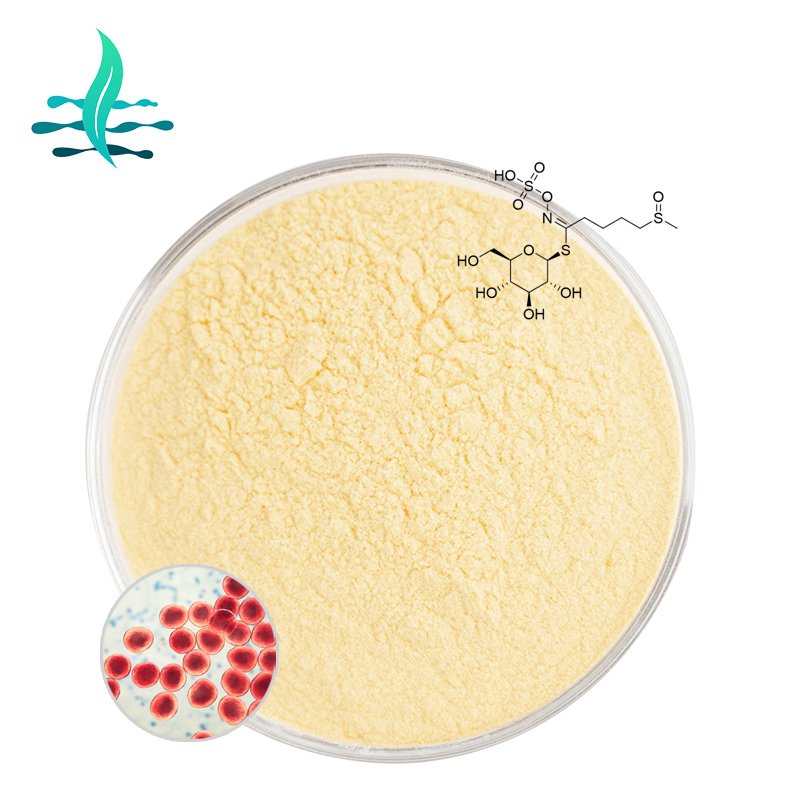
Extraction and transformation
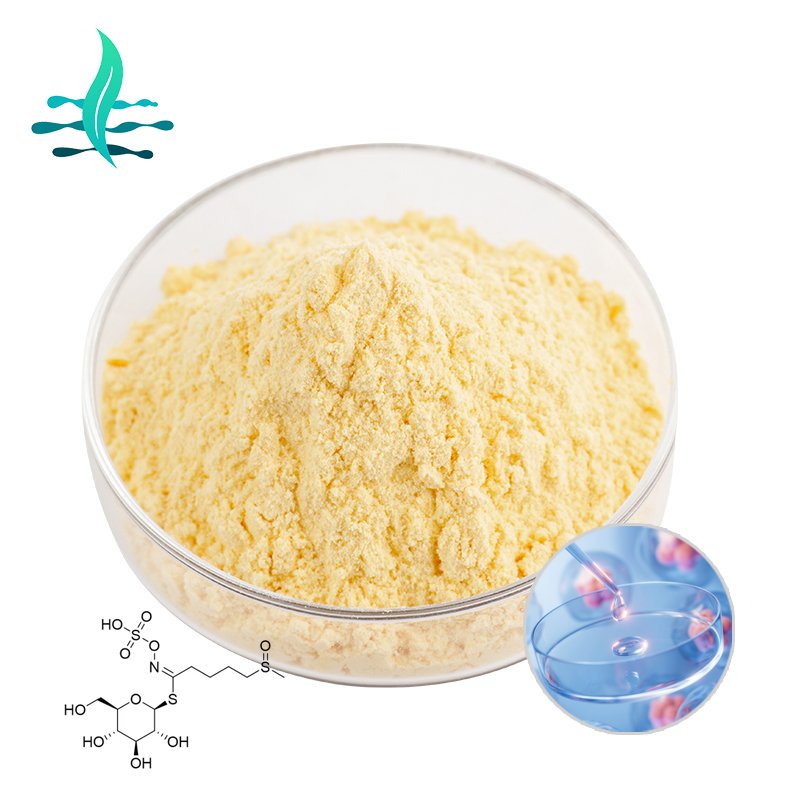
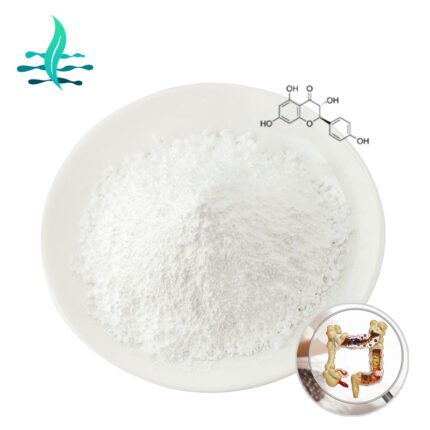
Extraction method: In order to obtain glucoraphanin, it is usually necessary to extract it from cruciferous vegetables. Appropriate process conditions need to be adopted during the extraction process to prevent the degradation and loss of glucoraphanin.
In vivo transformation: In the human body, glucoraphanin is mainly converted into sulforaphane by β-sulfosidase (myrosinase) contained in the probiotic flora in the intestine (such as Bacillus bulgaricus, Bifidobacterium, etc.), thereby exerting its biological activity. However, due to individual differences, the in vivo conversion efficiency of glucoraphanin is not ideal, usually varying from about 10% to 50%.